
元数据说明
- name: string --在模板中绑定时使用的管道名。通常使用 lowerCamelCase 拼写方式,因为名字中不允许包含减号(-)。
- pure?: boolean --为 true 时,该管道是纯管道,也就是说 transform() 方法只有在其输入参数变化时才会被调用。管道默认都是纯管道。
用法
{{ exp | myPipe }}
内置管道
Angular有很多内置管道供我们使用,下面是常用的内置管道(更多查看官方文档):- AsyncPipe --自动订阅模板中的Observable或Promise
- CurrencyPipe --把数字转换成金额字符串, 根据本地化规则进行格式化
- DatePipe --根据区域设置规则格式化日期值
- DecimalPipe --数字转字符串,并可以指定格式
- KeyValuePipe --使ngFor可以循环Object或Map对象
- JsonPipe --把一个值转换成JSON字符串格式。在调试时很有用。
- TitleCasePipe --把首字母大写,其它小写
- SlicePipe --截取Array或String
- PercentPipe --数字转百分比
- LowerCasePipe和UpperCasePipe --转化小写或大写
KeyValuePipe
以前我们ngFor的时候都是循环的数组,通过KeyValuePipe,我们可以循环Object或Map对象。
创建pipe组件:
ng g c components/pipe -s
创建普通对象以及Map对象:
// pipe.component.ts
...
export class PipeComponent implements OnInit {
obj:{[key: number]: string} = {2: 'foo', 1: 'bar'};
map = new Map([[2, 'foo'], [1, 'bar']]);
...
}
循环:
<!-- pipe.component.html -->
<div class="pipe">
<div *ngFor="let item of obj | keyvalue">
{{item.key}}: {{item.value}}
</div>
<div *ngFor="let item of map | keyvalue">
{{item.key}}: {{item.value}}
</div>
</div>
自定义管道
下面定义一个将数字指数化的管道exponentialStrength。如{{5 | exponentialStrength: 3}},表示5的3次方。
ng g p pipe/exponentialStrength
tips: 执行上面的命令后,cli工具会自动引入相应模块到app.module.ts中
修改代码:
// exponential-strength.pipe.ts
import { Pipe, PipeTransform } from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
// 管道名字
name: 'exponentialStrength'
})
export class ExponentialStrengthPipe implements PipeTransform {
// 实现transform方法,返回处理过后的数字
transform(value: number, exponent?: number): number {
return Math.pow(value, isNaN(exponent) ? 1 : exponent);
}
}
创建一个管道就这么简单,我们就能在任意模版中使用。
<!-- 5的3次方 -->
<p>{{5 | exponentialStrength: 3}}</p>
<!-- 8的1次方 -->
<p>{{8 | exponentialStrength}}</p>
非纯管道
- 默认的管道都是纯的,
Angular会忽略复合对象中的变化,即管道只会检查原始值或对象引用。
- 可如果数组中的元素变化,增删改,由于引用没有变化,所以不会执行管道的逻辑。
我们将通过下面一个简单的例子来说明这个问题。
ng g p pipe/numberGtZero
// number-gt-zero.pipe.ts
...
@Pipe({name: 'numberGtZero'})
export class NumberGtZeroPipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(arr: any[]): number[] {
const result: number [] = [];
arr.map(n => {
if (!isNaN(n) && n > 0) {
result.push(n);
}
});
return result;
}
}
// pipe.component.ts
export class PipeComponent implements OnInit {
numArr = [-6,7,6,-4,-3,0,3,1,-2];
// ...
addNumber() {
const plusOrMinus = Math.random() < 0.5 ? -1 : 1;
const randomNum = Math.floor(Math.random() * 10);
this.numArr.push(plusOrMinus * randomNum);
console.log(this.numArr);
}
}
<button class="btn btn-primary" (click)="addNumber()">添加数字</button><br>
<!-- 只显示大于0的数 -->
<span *ngFor="let n of (numArr | numberGtZero)">{{n}}</span>
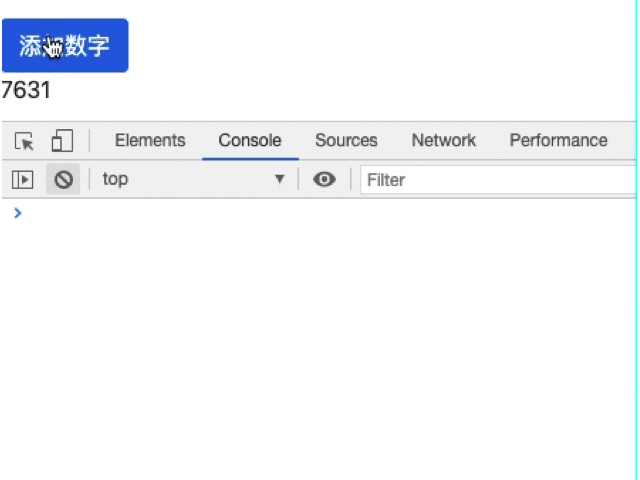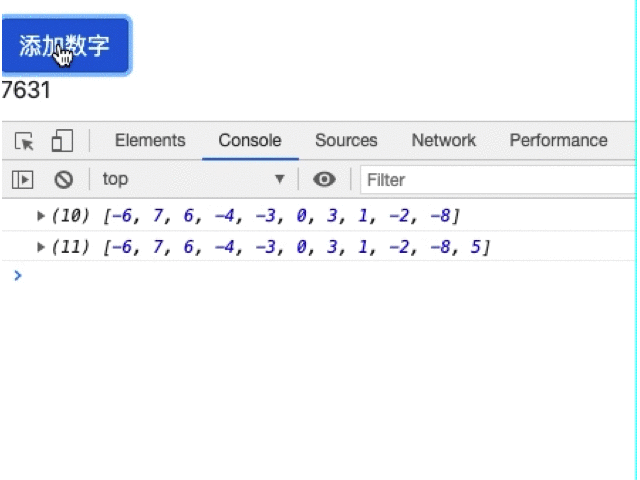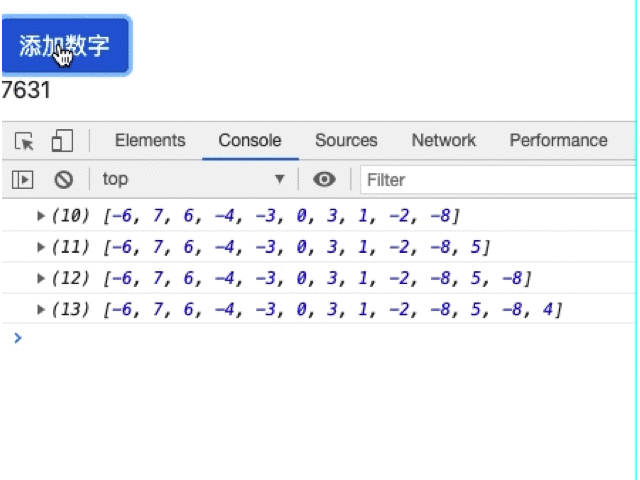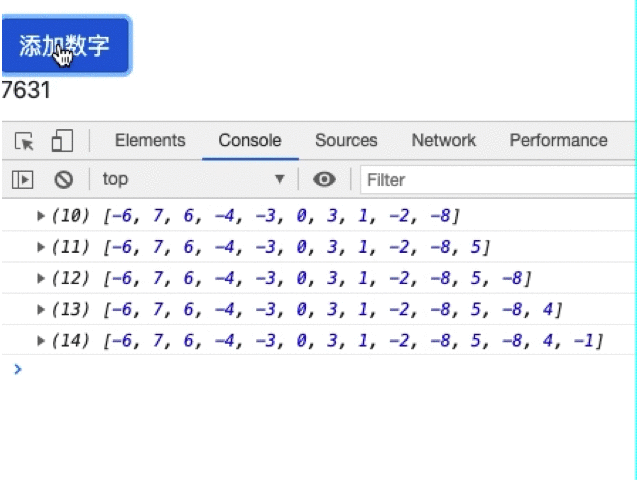
我们可以通过数组的操作来解决这个问题,但是最简便的方式肯定是官方的做法,修改pure参数为false:
// number-gt-zero.pipe.ts
...
@Pipe({
name: 'numberGtZero',
pure: false
})
总结
- 官方内置管道能满足日常基本需求,
KeyValuePipe用于循环对象、Map; - 自定义管道时,建议使用
cli命令生成模版,不然将手动引入组件是个麻烦事; - 当管道筛选的数据是复杂类型时,请将
pure参数设置为false。
本文转载自:公众号 岩弈 Angular教程,版权归原作者所有,本博客仅以学习目的的传播渠道,不作版权和内容观点阐述,转载时根据场景需要有所改动。






最新评论