
转换操作符
buffer
import { interval, fromEvent } from 'rxjs';
import { buffer } from 'rxjs/operators';
const myInterval = interval(1000);
const bufferBy = fromEvent(document, 'click');
/*
收集由 myInterval 发出的所有值,直到我们点击页面。此时 bufferBy 会发出值以完成缓存。
将自上次缓冲以来收集的所有值传递给数组。
*/
const myBufferedInterval = myInterval.pipe(buffer(bufferBy));
// 例如 输出: [1,2,3] ... [4,5,6,7,8]
const subscribe = myBufferedInterval.subscribe(val =>
console.log(' Buffered Values:', val)
);
bufferCount
bufferSize ),如果指定了第二个参数:startBufferEvery (上一轮索引),意味着每次新一轮的收集会从上一轮指定索引的位置开始复用。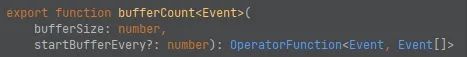
import { interval } from 'rxjs';
import { bufferCount } from 'rxjs/operators';
const source = interval(1000);
// 在发出3个值后,将缓冲的值作为数组传递
const bufferThree = source.pipe(bufferCount(3));
// 输出: [0,1,2]...[3,4,5]
const subscribe = bufferThree.subscribe(val =>
console.log('Buffered Values:', val)
);
import { interval } from 'rxjs';
import { bufferCount } from 'rxjs/operators';
fromEvent(document, 'click')
.pipe(
pluck('clientX'),
/*
* 页面点击3次,达到缓存限度,输出长度为3的数组,类似:[743, 709, 1154]
* 以后每点击一次,服用上一次从位置1开始的数组,类似:[743, 709, 560]
* */
bufferCount(3, 1)
)
.subscribe(res => console.log(res));
bufferTime
bufferTimeSpan ),才将其作为数组发出,如果指定了第二个参数:bufferCreationInterval (间隔时间),就会等待这个时间再次发送下一个流。import { interval } from 'rxjs';
import { bufferTime } from 'rxjs/operators';
const source = interval(500);
// 2秒后,将缓冲值作为数组发出
const example = source.pipe(bufferTime(2000));
// 输出: [0,1,2] [3,4,5,6] [7,8,9,10]...
const subscribe = example.subscribe(val =>console.log(val));
import { interval } from 'rxjs';
import { bufferTime } from 'rxjs/operators';
interval(500)
.pipe(
/*
* 在1秒时推送第一个流:[0]
* 此后,每等待3秒推送下一个:[5,6,7] [11,12,13]...
* */
bufferTime(1000, 3000)
)
.subscribe(res => console.log(res));
bufferToggle
import { interval } from 'rxjs';
import { bufferToggle } from 'rxjs/operators';
const sourceInterval = interval(1000);
const startInterval = interval(5000);
const closingInterval = val => {
console.log(`${val} 开始缓冲! 3秒后关闭`);
return interval(3000);
};
// 每5秒会开启一个新的缓冲区以收集发出的值,3秒后发出缓冲的值,并关闭当前缓冲区
const bufferToggleInterval = sourceInterval.pipe(
bufferToggle(
startInterval,
closingInterval
)
);
const subscribe = bufferToggleInterval.subscribe(val =>
console.log('Emitted Buffer:', val)
);
bufferWhen
Observable 发出值。import { interval } from 'rxjs';
import { bufferWhen } from 'rxjs/operators';
const oneSecondInterval = interval(1000);
const fiveSecondInterval = () => interval(5000);
// 每5秒发出缓冲的值
const bufferWhenExample = oneSecondInterval.pipe(bufferWhen(fiveSecondInterval));
// 输出: [0,1,2,3] [4,5,6,7,8]...
const subscribe = bufferWhenExample.subscribe(val =>
console.log('Emitted Buffer: ', val)
);
map
map ,对源 observable 的每个值进行映射。import { from } from 'rxjs';
import { map } from 'rxjs/operators';
const source = from([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
const example = source.pipe(map(val => val + 10));
const subscribe = example.subscribe(val => console.log(val));
mapTo
observable 的每个值映射成一个指定的值。import { interval } from 'rxjs';
import { mapTo } from 'rxjs/operators';
const source = interval(2000);
// 将所有发出值映射成同一个值
const example = source.pipe(mapTo('HELLO WORLD!'));
// 输出: 'HELLO WORLD!'...'HELLO WORLD!'...'HELLO WORLD!'...
const subscribe = example.subscribe(val => console.log(val));
switchMap
observable 发出的每个值,经过处理,映射成新的 observable ,但每次都会取消上一次的 observable ,不管上次 observable 是否完成。此操作符可以取消正在进行中的网络请求!import { fromEvent, interval } from 'rxjs';
import { switchMap } from 'rxjs/operators';
const clicks = fromEvent(document, 'click');
const result = clicks.pipe(switchMap((ev) => interval(1000)));
// 每次点击都会重新开始执行interval的流,从0开始打印值
result.subscribe(x => console.log(x));
switchMapTo
observable 发出的每个值,经过处理,映射成固定的值(不限于 observable )import { fromEvent } from 'rxjs';
import { switchMapTo } from 'rxjs/operators';
const clicks = fromEvent(document, 'click');
const result = clicks.pipe(switchMapTo('hello'));
// 每次点击打印出'hello'
result.subscribe(x => console.log(x));
concatMap & mergeMap
observable 发出的每个值,按顺序映射成一个新的 observable。import { of } from 'rxjs';
import { concatMap, delay, mergeMap } from 'rxjs/operators';
const source = of(2000, 1000);
// 将内部 observable 映射成 source,当前一个完成时发出结果并订阅下一个
const example = source.pipe(
concatMap(val => of(`Delayed by: ${val}ms`).pipe(delay(val)))
);
// 输出: With concatMap: Delayed by: 2000ms, With concatMap: Delayed by: 1000ms
const subscribe = example.subscribe(val =>
console.log(`With concatMap: ${val}`)
);
// 展示 concatMap 和 mergeMap 之间的区别
const mergeMapExample = source
.pipe(
// 只是为了确保 meregeMap 的日志晚于 concatMap 示例
delay(5000),
mergeMap(val => of(`Delayed by: ${val}ms`).pipe(delay(val)))
)
.subscribe(val => console.log(`With mergeMap: ${val}`));
concatMap 和 mergeMap 之间的区别:concatMap 之前前一个内部 observable 完成后才会订阅下一个, source 中延迟 2000ms 值会先发出。对比的话, mergeMap 会立即订阅所有内部 observables, 延迟少的 observable (1000ms) 会先发出值,然后才是 2000ms 的 observable 。concatMapTo & mergeMapTo
observable 发出的每个值,按顺序映射成一个固定值(不限于 observable )。import { fromEvent, interval } from 'rxjs';
import { concatMapTo, mergeMapTo, take } from 'rxjs/operators';
fromEvent(document, 'click').pipe(
concatMapTo(interval(1000).pipe(take(2)))
).subscribe(
// 每次点击,隔1秒输出0,再间隔1秒输出1,流发射结束
res => console.log(res)
);
fromEvent(document, 'click').pipe(
mergeMapTo(interval(1000).pipe(take(2)))
).subscribe(
// 每次点击,都会出发interval发射流
res => console.log(res)
);
scan
observable 上应用累加器函数,每次累加后返回一个 observable 。// 随着时间的推移计算总数
import { of, Subject } from 'rxjs';
import { scan } from 'rxjs/operators';
const source = of(1, 2, 3);
// 基础的 scan 示例,从0开始,随着时间的推移计算总数
const example = source.pipe(scan((acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0));
// 输出每次累加值: 1,3,6
const subscribe = example.subscribe(val => console.log(val));
// 对对象进行合并
const subject = new Subject();
subject.pipe(
scan((acc, value) => Object.assign({}, acc, value), {})
).subscribe(
res => console.log(res)
);
// subject 发出的值会被添加成对象的属性
// {name: 'Joe'}
subject.next({ name: 'Joe' });
// {name: 'Joe', age: 30}
subject.next({ age: 30 });
// {name: 'Joe', age: 30, favoriteLanguage: 'JavaScript'}
subject.next({ favoriteLanguage: 'JavaScript' });
mergeScan
scan , 在源 Observable 上应用累加器函数,每次累加后返回一个 Observable 。import { of } from 'rxjs';
import { mergeScan } from 'rxjs/operators';
of(1, 2, 3).pipe(
mergeScan((acc, value) => of(acc + value), 0)
).subscribe(
res => console.log(res)
);
reduce
Array.prototype.reduce() , 也类似 scan ,只不过会等源 observable 完成时将结果发出。import { of } from 'rxjs';
import { reduce } from 'rxjs/operators';
const source = of(1, 2, 3);
const example = source.pipe(reduce((acc, val) => acc + val));
// 输出最后累加结果:6
const subscribe = example.subscribe(val => console.log('Sum:', val));
pluck
import { from } from 'rxjs';
import { pluck } from 'rxjs/operators';
const source = from([
{ name: 'Joe', age: 30, job: { title: 'Developer', language: 'JavaScript' } },
// 当找不到 job 属性的时候会返回 undefined
{ name: 'Sarah', age: 35 }
]);
// 提取 job 中的 title 属性
const example = source.pipe(pluck('job', 'title'));
// 输出: "Developer" , undefined
const subscribe = example.subscribe(val => console.log(val));
pairwise
import { interval } from 'rxjs';
import { pairwise } from 'rxjs/operators';
// 输出:[0, 1] [1, 2]...
interval(1000).pipe(pairwise()).subscribe(res => console.log(res));
groupBy
Observable 按条件按组发出。(这个就很有用了)import { from } from 'rxjs';
import { groupBy, mergeMap, toArray } from 'rxjs/operators';
const people = [
{ name: 'Sue', age: 25 },
{ name: 'Joe', age: 30 },
{ name: 'Frank', age: 25 },
{ name: 'Sarah', age: 35 }
];
// 发出每个 people
const source = from(people);
// 根据 age 分组
const example = source.pipe(
groupBy(person => person.age),
// 为每个分组返回一个数组
mergeMap(group => group.pipe(toArray()))
);
/*
输出:
[{age: 25, name: "Sue"},{age: 25, name: "Frank"}]
[{age: 30, name: "Joe"}]
[{age: 35, name: "Sarah"}]
*/
const subscribe = example.subscribe(val => console.log(val));
exhaust
Observable 为完成前,忽略所有其它的 Observable 。import { fromEvent, interval } from 'rxjs';
import { exhaust, map, take } from 'rxjs/operators';
const clicks = fromEvent(document, 'click');
const higherOrder = clicks.pipe(
map((ev) => interval(1000).pipe(take(5))),
);
const result = higherOrder.pipe(exhaust());
// 不管点击多少次,都会先完成上一次未完成的interval的流
result.subscribe(x => console.log(x));
exhaustMap
map + exhaust的结合,比如上个例子可简写为:import { fromEvent, interval } from 'rxjs';
import { exhaustMap, take } from 'rxjs/operators';
const clicks = fromEvent(document, 'click');
const higherOrder = clicks.pipe(
exhaustMap(ev => interval(1000).pipe(take(5)))
);
higherOrder.subscribe(x => console.log(x));






最新评论